VPS Command and Control
IO Coop VPS’s have a system in place to allow you to remotely reboot/shutdown/console your VPS’s.
Access is controlled via the sshkey provided when signing up for the VPS.
ssh -t vps@g1.iocoop.org
==================================================== IO Coop VPS command and control ==================================================== Commands: list List all available instance. console Attach to the serial console of an instance. reboot Reboot an instance. startup Start an instance. shutdown Shutdown an instance. vncconsole Expose a VNC port to connect to an instance's console.
How to remotely access your VPS graphical desktop using VNC
VNC is a graphical desktop sharing system. With it you can connect to your VPS to diagnose problems when you’ve lost access to it through other means (ssh, web)
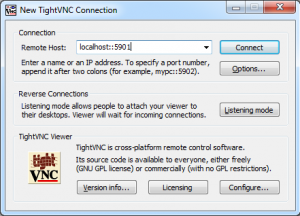
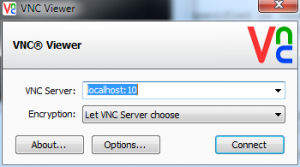
- Install a VNC client. TightVNC is a good Windows client and RealVNC works on Mac Windows and Linux
- Determine what port your VPS is bound to.
ssh -t vps@g0.iocoop.org list
- This command will connect to the VPS management system and list out the VPS or VPSs that you have
============================================================================= IO Coop VPS command and control ============================================================================= Commands: list List all available instance. console <instance> Attach to the serial console of an instance. reboot <instance> Reboot an instance. startup <instance> Start an instance. shutdown <instance> Shutdown an instance. vncconsole <instance> Expose a VNC port to connect to an instance's console. user@example.com> list Instance Name State CPUs RAM VNC Port ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- myhost.example.com running 1 2048 localhost:12345
- In this example our VPS is called myhost.example.com and the “VNC Port” is “localhost:12345” however your VPS name and VNC port will be different.
- This command will connect to the VPS management system and list out the VPS or VPSs that you have
- Establish a SSH tunnel between your computer and the VPS management system over the VNC port.
ssh -t -L 12345:localhost:12345 vps@g0.iocoop.org vncconsole myhost.example.com
- With this command we’re creating a tunnel between port 12345 on our host and port 12345 on the VPS management system. This will allow us to connect our VNC client to the VPS management system
- Run your VNC client
- Connect to “localhost:12345” in your VNC client
How to remotely access your VPS console
You can access your VPS host over serial console by running
ssh -t vps@g1.iocoop.org console myhost.example.com
Once you do, you’ll get back this response
INFO: Original command Console for: 'alpha.rogerklorese.com' Use ^] to disconnect (You might need to press enter to wake up the getty on your instance) -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
At this point, hit the enter key to get a prompt from your host and then login with your user.
Last updated: 2024-10-18 09:08:41 by troy